Raman Microscopes
Micro Raman Spectroscopy
with up to 1 μm spatial resolution
RamanLife Raman microscope is an optical device that conveniently and effectively combines the advanced technological capabilities of a Raman spectrometer and an optical microscope. Such an integrated instrument offers a critical advantage over conventional spectrometers. In this system, the spectral micro Raman signal is collected from a micron-size focal region illuminated by the excitation laser. Therefore, the measurements can be highly localized, which enables spatial scanning across the sample surface, with distinct spectra representing various points of interest.
Typical Raman microscope parameters
| Laser |
532 nm
637 nm
|
785 nm
|
1064 nm
|
| Spectral range |
120-4000 cm-1 |
120-2700 cm-1 |
150-1800 cm-1 |
| Spectral resolution |
4 - 6 cm-1 |
6 - 8 cm-1 |
6 - 8 cm-1 |
| Spatial resolution | 1 μm 10x, 20x, 40x, and 50x objectives included |
||
| Options |
|
||
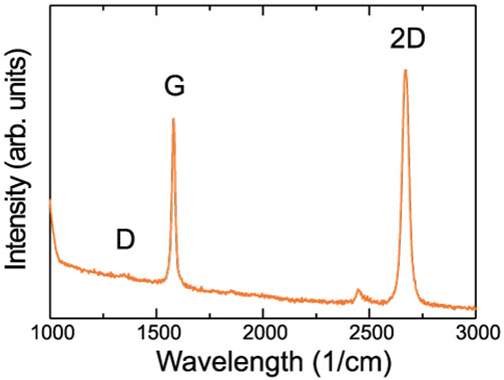
Example of micro Raman studies
Micro Raman spectroscopy
Raman spectral imaging is a powerful technique for rendering detailed chemical mapping based on the Raman microscopy of a sample. As a full Raman spectrum is acquired at each measurement point on a specimen, the resultant array of spectra makes possible construction of a color visualization reflecting the composition and structure of the material. In particular,
- the intensity data of the Raman peak spectra provide a pictorial description of the density distribution of matter;
- the specific position of the Raman peak across the set of spectra illustrates the molecular structure and phase, as well as internal stresses;
- the width of the Raman peak reveals the peculiarities of the crystalline structure and phase.
Micro Raman mapping likewise enables the characterization of a sample at the level beyond the capabilities of traditional optical microscopy. For example, given images can be readily used to determine:
- the distribution of components as well as the grain or particle size;
- the variations in the crystalline structure or phase of a sample;
- the shape and size of intrinsic impurities;
- the interaction and association of components across the interphase boundary;
- the distribution of internal stresses and deformations in a sample.
Raman Spectra Library
Raman spectroscopy can uniquely identify many chemical and biological agents.
All substancesMicro Raman resolution
In practice, the maximum achievable spatial resolution of a Raman microscope is dictated by the laser wavelength and parameters of the microscope lens, and in theory, it is restricted by the diffraction limit. Therefore, according to the laws of optical physics, the planar spatial resolution, R can be defined as:
R =0.61* λ / NA,
where λ is the laser wavelength, and is the numerical aperture of the lens. From this relation, it is evident that the spatial resolution of the Raman microscope is directly proportional to the laser wavelength and inversely proportional to the numerical aperture of the lens. Thus, to put it in the context of an actual system — a Raman microscope with a standard 532-nm laser and 0.90/100x lens can reach a remarkable level of spatial resolution at 361 nm.