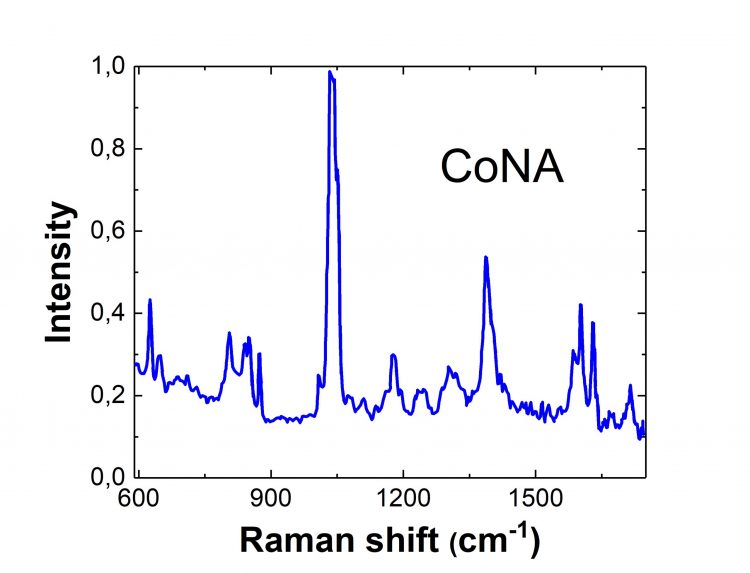
Cobalt Raman Spectrum
Cobalt (Co) is a ferromagnetic metal with the Curie temperature TC=1,115 °C. It is a weakly reducing metal protected against oxidation by a passivating oxide film. Cobalt is used primarily to manufacture magnetic, wear-resistant, and high-strength alloys; in lithium-ion batteries; in electroplating, for its hardness, resistance to oxidation, and attractive appearance; and as a base primer coating for porcelain enamels. Co also plays an essential role in the metabolism of all animals because it is a key component in cobalamin (vitamin B12).
Contact us to get access to Raman Spectra Database more than 20 000 chemical and biological substances
Raman spectroscopy of Co
In biology, cobalt is more commonly found in complex forms. For example, nicotinic acid aids digestion helping the body derive energy from fats, proteins, and carbohydrates. It has unique pharmacological properties for treating asthma, arthritis, diabetes, providing anti-aging nutrients, and preventing heart diseases. That is why the complex formation of the nicotinic acid and metal ions (e.g., cobalt (II)) is of great interest to science, in which case, the Raman spectroscopy of the complex can be used to determine its structure.
Raman Spectra Library
Raman spectroscopy can uniquely identify many chemical and biological agents.
All substances