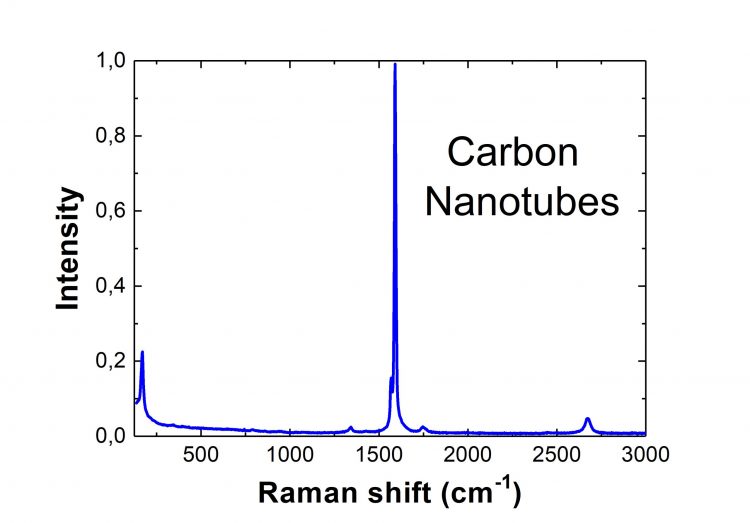
Carbon Nanotubes Raman Spectrum
A single-wall carbon nanotube is an atom-thick layer of graphite crystal rolled up into a seamless cylinder. Usually, it has approximately 10–40 carbon atoms along the circumference and a considerable axial length on the order of microns. Carbon nanotubes are involved in numerous applications related to energy storage, automotive parts, device modeling, sporting goods, boat hull construction, water filters, coatings, thin-film electronics, designing actuators, and electromagnetic shields.
Contact us to get access to Raman Spectra Database more than 20 000 chemical and biological substances
Raman spectroscopy of Carbon Nanotubes
Carbon nanotubes have proven to be unique in facilitating the study of Raman spectra in one-dimensional systems. At the same time, Raman spectroscopy has become an exceedingly powerful tool for characterizing single-wall carbon nanotubes. Thus, the Raman spectroscopy of carbon nanotubes can provide us with a great deal of information regarding the exceptional 1D properties of carbon materials, such as their electronic and phonon structure, as well as sample imperfections like physical defects.
Raman Spectra Library
Raman spectroscopy can uniquely identify many chemical and biological agents.
All substances