SERS biosensors may control the spread of COVID-19

The key to controlling the spread of COVID-19 is precise and rapid detection of blood antibodies against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). Lateral flow immunoassay (LFIA) is one of the most popular methods for serological testing of anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgM/IgG due to its simplicity, adaptability, rapidity, and low cost. In the article "Development of a SERS-based lateral flow immunoassay for rapid and ultra-sensitive detection of anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgM/IgG in clinical samples", published in Sensors and Actuators, B: Chemical, scientists developed a novel SERS-LFIA biosensor for the high-sensitivity and simultaneous analysis of anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgM/IgG.
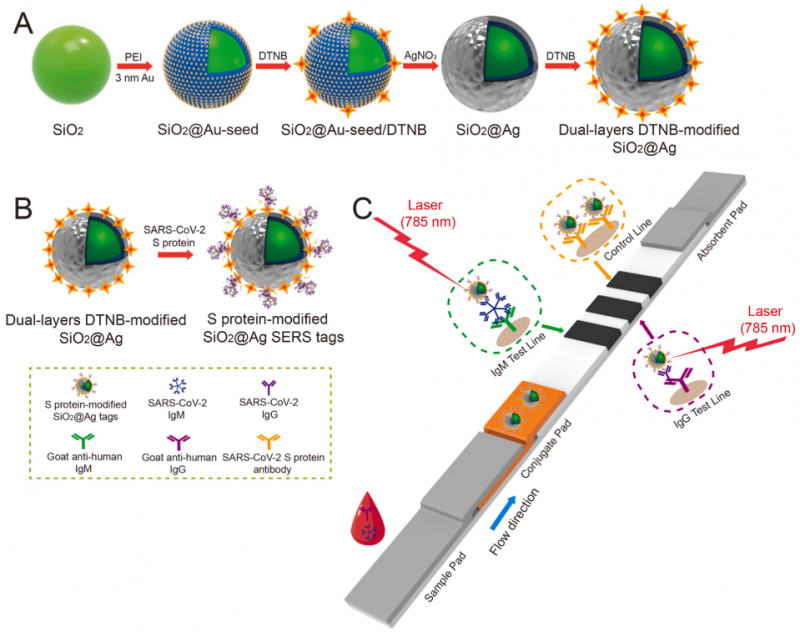
Authors created SiO2 nanoparticles coated with Ag (SiO2@Ag NPs) as advanced SERS tags in clinical samples (see Fig.1 (A)). Anti-human IgM, anti-human IgG, and anti-S protein antibodies were dispensed on three test lines built in the LFIA strip (see Fig.1 (C)). The solution of the clinical sample with virus-specific IgM and IgG antibodies and the running buffer drops on the strip. It migrates along the strip toward the test lines, and SERS tags capture specific IgM and IgG. Formed complexes give intense lines in the Raman spectrum. Thus, this technique simultaneously detects anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgM/IgG in human serum based on typical antibody-antigen reactions.
Figure 1. (A) Schematic illustration of the dual-layers SiO2@Ag NPs preparation. (B) SARS-CoV-2 S protein-modified SiO2@Ag SERS tags preparation. (C) The SERS-LFIA strip's operating concept for high-sensitivity and simultaneous anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgM/IgG analysis. Adopted from here.